IDApython 在日常逆向的过程中是十分重要的存在,过去零零散散的接触过一些 idapython, 但是我觉得还是有必要去系统的整理一下相关的函数,以便未来倘若忘记了可以快速通过这篇笔记回忆起来
# 官方文档
- IDA Help: Alphabetical list of IDC functions
- IDAPython documentation
# IDApython 编写环境
- PyCharm 2021.2.3 社区版
- IDA7.7
- python3.8
由于 IDA 自带的 IDE 没有代码补全十分的难用,所以我准备在 PyCharm 中编写 IDApython 代码
在 pycharm 中进入到 文件-->设置-->项目: xxx.py-->Python解释器 ,然后点击此处的 全部显示 如图
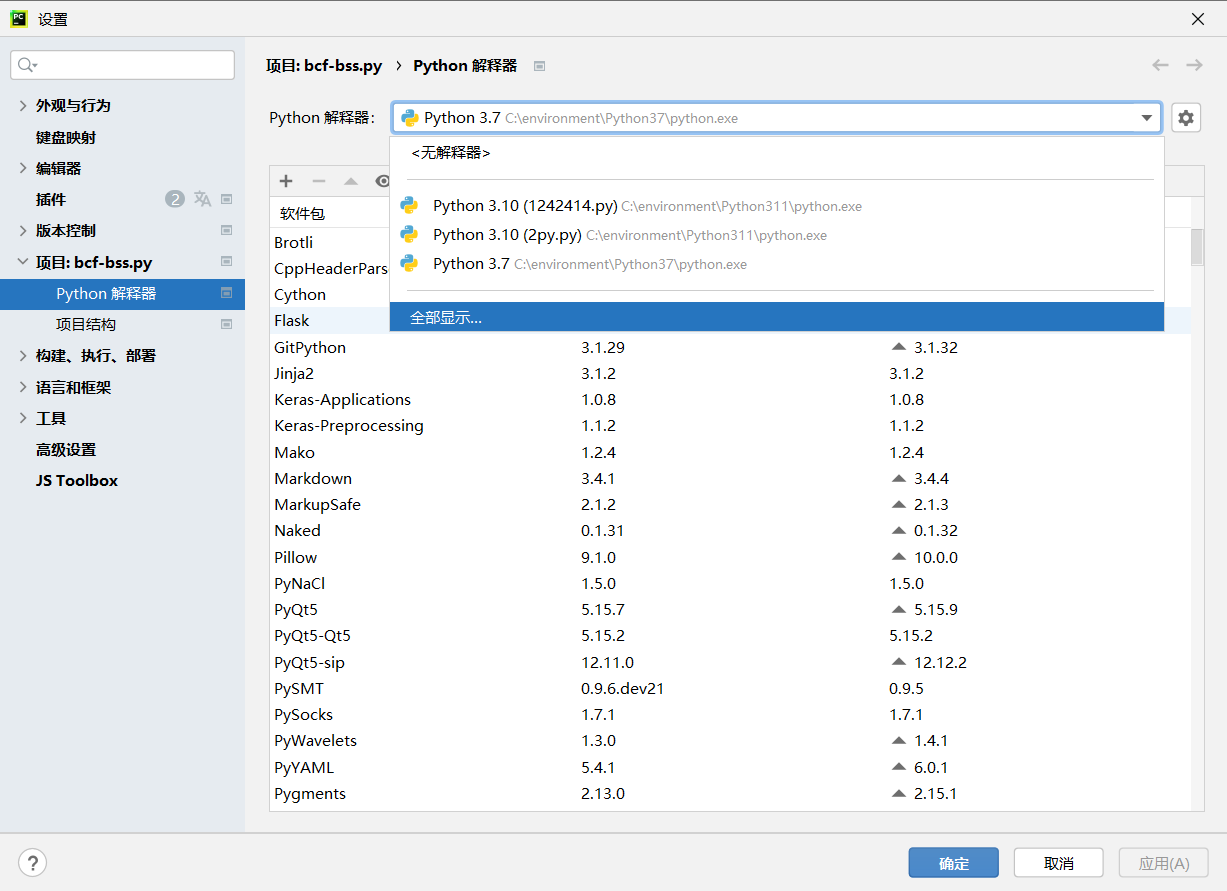
然后点击该位置来添加自定义路径
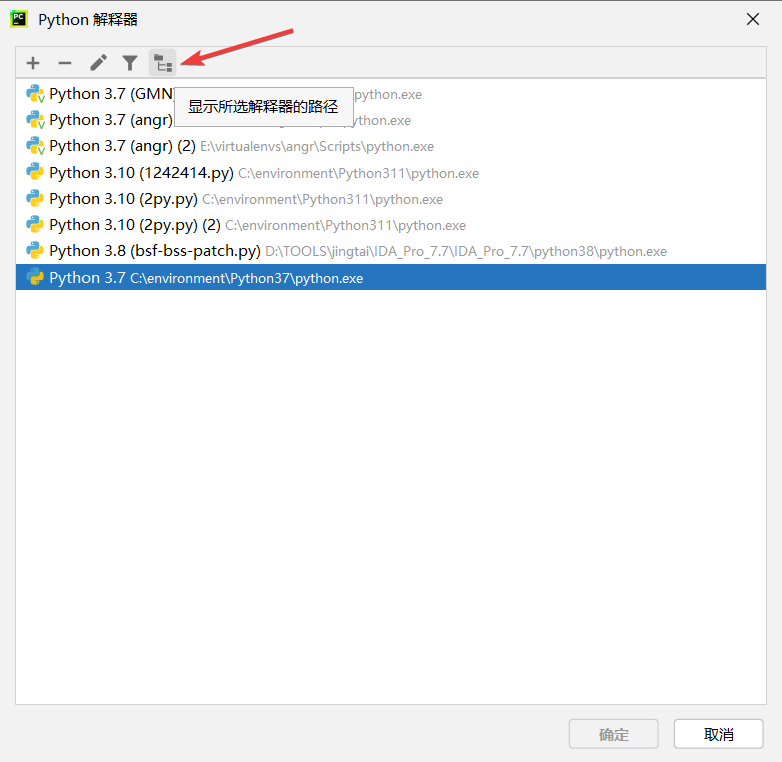
将 IDA安装路径\python\3 添加至解释器路径中如图
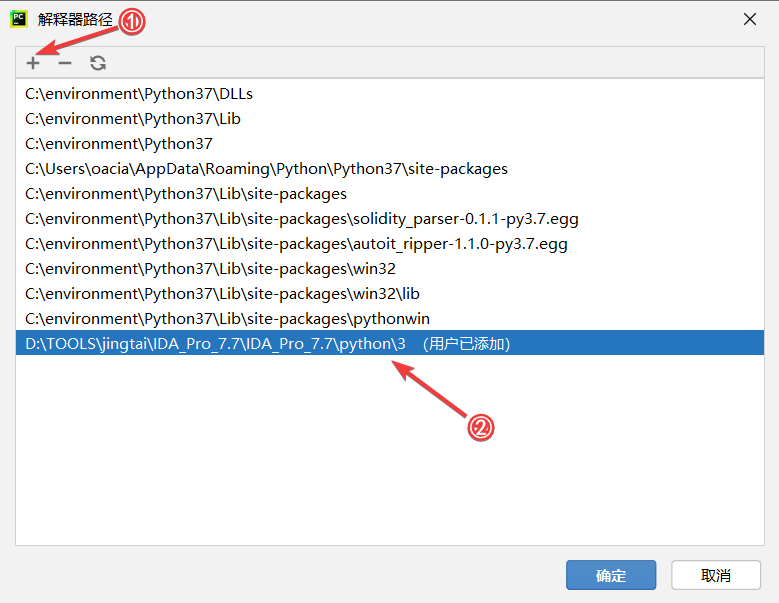
点击确定之后,在 Pycharm 中即可实现 IDApython 代码补全
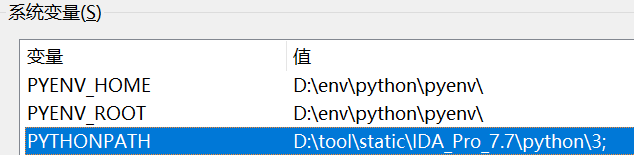
当然啦,我们也可以直接在 windows 中添加 PYTHONPATH 的环境变量,同样可以做到 idapython 的代码补全
# 地址 address
idc.get_screen_ea()#获取当前光标所在地址 |
idc.get_inf_attr(INF_MAX_EA)#获取本文件的最大地址 | |
idc.get_inf_attr(INF_MIN_EA)#获取本文件的最小地址 | |
idaapi.get_imagebase()#获取文件的基址 | |
idc.next_head(ea)/idc.prev_head(ea)#获取下一条 / 上一条指令的地址 |
# 判断当前地址是否在程序中存在 | |
if idaapi.BADADDR != ea: | |
print("valid address") |
# 反汇编 disasm
idc.GetDisasm(ea)#获取某一个地址的反编译汇编指令 | |
idc.print_insn_mnem(ea)#返回助记符,get mnemonic | |
idc.print_operand(ea,n)#返回第 n + 1 个参数 | |
idc.get_operand_value(ea,n)#返回第 n + 1 个参数的数值形式 | |
idc.get_item_size(ea)#获取某行汇编的长度 |
举个例子
ea = here() | |
print(idc.GetDisasm(ea))# mov eax, [rbp+var_4] | |
print(idc.print_insn_mnem(ea))# mov | |
print(idc.print_operand(ea, 0))# eax | |
print(idc.print_operand(ea, 1))# [rbp+var_4] |
# 段 segment
idc.get_segm_name(ea)#获取地址所在段的段名 | |
idc.get_segm_start(ea)/idc.get_segm_end(ea)#获取地址所在段起始 / 结束地址 | |
idautils.Segments()#获取所有的段首地址 | |
idc.get_first_seg()/idc.get_next_seg() # 获取第一个段 / 下一个段的地址 | |
idc.get_segm_attr(ea,attr)/idc.set_segm_attr(ea,attr,value) # 获取 / 设置函数的属性 | |
ida_segment.get_segm_by_name('.text')#通过 name 来获取段对象 |
举个例子
#遍历所有的段 | |
for i in idautils.Segments(): | |
print(f"%s:\t0x%x\t0x%x" %( | |
idc.get_segm_name(i), | |
idc.get_segm_start(i), | |
idc.get_segm_end(i))) |
# 通过名称来获取段对象 | |
sg = ida_segment.get_segm_by_name('.text') | |
print(sg.start_ea,sg.end_ea,sg.size()) |
# 函数 function
idc.get_func_name(ea)#通过地址获取函数名 | |
idaapi.get_func(ea)#通过地址获取地址所在的函数 | |
idc.get_next_func(ea)/idc.get_prev_func(ea) # 获取当前函数的前一个 / 后一个函数的地址 | |
idautils.Functions(start, end)#获取所有函数的首地址,若没有参数,则默认从头到尾 | |
idc.get_func_attr(func, FUNCATTR_FLAGS)#检索函数的信息 |
举个例子
#遍历所有函数 | |
for func in idautils.Functions(): | |
print(hex(func), idc.get_func_name(func),sep=':') |
#获取函数的起始 / 结束地址 | |
func = idaapi.get_func(ea) | |
print(func.start_ea, func.end_ea) |
#检索关于函数的信息,来判断该函数是否是库中代码,或者函数是否有返回值等等 | |
for func in idautils.Functions():#获取所有已知的函数首地址 | |
flags = idc.get_func_attr(func, FUNCATTR_FLAGS)#获取标志 | |
if flags & FUNC_NORET: | |
print(hex(func), get_func_name(func), "FUNC_NORET") | |
if flags & FUNC_FAR: | |
print(hex(func), get_func_name(func),"FUNC_FAR") | |
if flags & FUNC_LIB: | |
print(hex(func), get_func_name(func),"FUNC_LIB") | |
if flags & FUNC_STATIC: | |
print(hex(func), get_func_name(func),"FUNC_STATIC") | |
if flags & FUNC_FRAME: | |
print(hex(func), get_func_name(func),"FUNC_FRAME") | |
if flags & FUNC_USERFAR: | |
print(hex(func), get_func_name(func),"FUNC_USERFAR") | |
if flags & FUNC_HIDDEN: | |
print(hex(func), get_func_name(func),"FUNC_HIDDEN") | |
if flags & FUNC_THUNK: | |
print(hex(func), get_func_name(func),"FUNC_THUNK") | |
if flags & FUNC_LIB: | |
print(hex(func), get_func_name(func),"FUNC_BOTTOMBP") |
各个函数标志的含义如下
| 函数标志 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| FUNC_NORET | 这个标志表示某个函数是否有返回值,它本身的值是 1,下面是一个没有返回值的函数,注意它没有函数的最后并不是 ret 或者 leave 指令。 |
| FUNC_FAR | 这个标志非常少的出现,标志程序是否使用分段内存,它的值为 2。 |
| FUNC_USERFAR | 少见 |
| FUNC_LIB | 这个表示用于寻找库函数的代码。识别库函数代码是非常有必要的,因为我们在分析的时候一般将其跳过,它的值是 4。 |
| FUNC_STATIC | 静态函数 |
| FUNC_FRAME | 这个标志表示函数是否使用了 ebp 寄存器 (帧指针),使用 ebp 寄存器的函数通常有如下的语法设定,目的是为了保存栈帧。 |
| FUNC_BOTTOMBP | 和 FUNC_FRAME 一样,该标志用于跟踪帧指针 (ebp)。它作用是识别函数中帧指针是 否等于堆栈指针 (esp)。 |
| FUNC_HIDDEN | 带有 FUNC_HIDDEN 标志的函数意味着它们是隐藏的,这个函数需要展开才能查看。如 果我们跳转到一个标记为 HIDDEN 的地址的话,它会自动的展开。 |
| FUNC_THUNK | 表示这个函数是否是一个 thunk 函数,thunk 函数表示的是一个简单的跳转函数。 |
# 块 block
遍历一个函数中的块
import idaapi | |
import idc | |
f_blocks = idaapi.FlowChart(idaapi.get_func(0x401E80), flags=idaapi.FC_PREDS) | |
for block in f_blocks: | |
print(hex(block.start_ea),hex(block.end_ea),hex(idc.prev_head(block.end_ea)),block.id)# 特别注意,block.end_ea 表示下一个块的起始地址,并不是当前块的结束地址!!,idc.prev_head (block.end_ea) 才是获取这个块的结束地址 |
获取 block 的前驱块
import idaapi | |
f_blocks = idaapi.FlowChart(idaapi.get_func(0x401E80), flags=idaapi.FC_PREDS) | |
block = f_blocks[1] | |
# 获取当前块的前驱块 | |
for pred in block.preds(): | |
print("前驱块",hex(pred.start_ea),pred.id) |
获取 block 的后继块
import idaapi | |
f_blocks = idaapi.FlowChart(idaapi.get_func(0x401E80), flags=idaapi.FC_PREDS) | |
block = f_blocks[1] | |
# 获取当前块的后继块 | |
for succ in block.succs(): | |
print("后继块",hex(succ.start_ea),succ.id) |
获取块的开始地址和结束地址
import idaapi | |
f_blocks = idaapi.FlowChart(idaapi.get_func(0x401E80), flags=idaapi.FC_PREDS) | |
block = f_blocks[1] | |
print (hex (block.start_ea),hex (idc.prev_head (block.end_ea)))# 获取块的开始地址 / 结束地址 |
# 操作数
可以通过 idc.get_operand_type(curr_addr, n) 获取第 n+1 个操作数的类型,返回值有八种情况,值和含义如下
| 操作数 | 值 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| o_void | 0 | 指令没有任何操作数,如 retn |
| o_reg | 1 | 操作数是寄存器 |
| o_mem | 2 | 操作数是直接寻址的内存,这种类型对寻找 DATA 的引用非常有帮助。如 cmp ds:dword_A152B8, 0 |
| o_phrase | 3 | 操作数是利用基址寄存器和变址寄存器的寻址操作的话,如 mov [edi+ecx], eax |
| o_displ | 4 | 操作数是利用寄存器和位移的寻址操作的话,如 mov eax, [edi+18h] |
| o_imm | 5 | 操作数是一个确定的数值,如 add esp, 0Ch |
| o_far | 6 | 这种返回类型在 x86 和 x86_64 的逆向中不常见。它用来判断直接访问远端地址的操作数 |
| o_near | 7 | 这种返回类型在 x86 和 x86_64 的逆向中不常见。它用来判断直接访问近端地址的操作数 |
# 判断在 curr_addr 的指令的第一个操作数的类型是否为利用寄存器和位移的寻址操作 | |
insn = ida_ua.insn_t() | |
idaapi.decode_insn(insn, curr_addr) | |
if insn.Op1.type == idaapi.o_displ: | |
print("第一个操作数的类型是利用寄存器和位移的寻址操作!") |
# insn 的各个属性 | |
Python>dir(insn) | |
['Op1', 'Op2', 'Op3', 'Op4', 'Op5', 'Op6', '__class__', '__delattr__', '__dict__', '__dir__', '__doc__', '__eq__', '__format__', '__ge__', '__get_auxpref__', '__get_operand__', '__get_ops__', '__getattribute__', '__getitem__', '__gt__', '__hash__', '__init__', '__init_subclass__', '__iter__', '__le__', '__lt__', '__module__', '__ne__', '__new__', '__reduce__', '__reduce_ex__', '__repr__', '__set_auxpref__', '__setattr__', '__sizeof__', '__str__', '__subclasshook__', '__swig_destroy__', '__weakref__', 'add_cref', 'add_dref', 'add_off_drefs', 'assign', 'auxpref', 'create_op_data', 'create_stkvar', 'cs', 'ea', 'flags', 'get_canon_feature', 'get_canon_mnem', 'get_next_byte', 'get_next_dword', 'get_next_qword', 'get_next_word', 'insnpref', 'ip', 'is_64bit', 'is_canon_insn', 'is_macro', 'itype', 'ops', 'segpref', 'size', 'this', 'thisown'] |
# 搜索
idc.FindBinary(ea,flag, searchstr, radix=16)#字节或者二进制的搜索 |
idc.FindBinary(ea,flag, searchstr, radix=16) 中 flag 的各个类型的含义
| 类型 | 值 | 含义 |
|---|---|---|
| SEARCH_UP | 0 | 向上搜索 |
| SEARCH_DOWN | 1 | 向下搜索 |
| SEARCH_NEXT | 2 | 获取下一个已经找到的对象 |
| SEARCH_CASE | 4 | 指明是否区分大小写 |
| SEARCH_REGEX | 8 | 正则搜索 |
| SEARCH_NOBRK | 16 | |
| SEARCH_NOSHOW | 32 | 指明是否显示搜索的进度 |
| SEARCH_UNICODE | 64 | 将所有搜索字符串视为 Unicode |
| SEARCH_IDENT | 128 | |
| SEARCH_BRK | 256 | |
举个例子
pattern = '55 48 89 E5' | |
addr = ida_ida.inf_get_min_ea() | |
for x in range(0,5): | |
addr = idc.find_binary(addr, SEARCH_DOWN|SEARCH_NEXT, pattern) | |
if addr != idc.BADADDR: | |
print(hex(addr), idc.GetDisasm(addr)) |
# 数据
ida_bytes.get_bytes(ea,size) | |
ida_bytes.get_byte(ea) | |
ida_bytes.get_word(ea) | |
ida_bytes.get_dword(ea) | |
ida_bytes.get_qword(ea) |
# 动态调试
idc.add_bpt(long Address)#在指定的地址设置断点 | |
idc.get_reg_value(string Register)#获取一个寄存器的名称 | |
idc.set_reg_value(long Value, string Register)#设置寄存器的值 | |
idc.run_to(long Address)#运行到指定的地址,然后停下。 | |
idc.wait_for_next_event(wfne,timeout)#等待下一个事件,此函数会继续执行进程,并等待调试器事件直到超时 |
在 idc.wait_for_next_event(wfne,timeout) 中参数即返回值的标志如下
-
wfne标志// wfne flag is combination of the following:#define WFNE_ANY 0x0001 // return the first event (even if it doesn't suspend the process)// if the process is still running, the database// does not reflect the memory state. you might want// to call refresh_debugger_memory() in this case#define WFNE_SUSP 0x0002 // wait until the process gets suspended#define WFNE_SILENT 0x0004 // 1: be slient, 0:display modal boxes if necessary#define WFNE_CONT 0x0008 // continue from the suspended state#define WFNE_NOWAIT 0x0010 // do not wait for any event, immediately return DEC_TIMEOUT// (to be used with WFNE_CONT)#define WFNE_USEC 0x0020 // timeout is specified in microseconds// (minimum non-zero timeout is 40000us) -
timeout,等待的秒数,-1 为无限大 -
返回值
debugger event codes// debugger event codes#define NOTASK -2 // process does not exist#define DBG_ERROR -1 // error (e.g. network problems)#define DBG_TIMEOUT 0 // timeout#define PROCESS_STARTED 0x00000001 // New process started#define PROCESS_EXITED 0x00000002 // Process stopped#define THREAD_STARTED 0x00000004 // New thread started#define THREAD_EXITED 0x00000008 // Thread stopped#define BREAKPOINT 0x00000010 // Breakpoint reached#define STEP 0x00000020 // One instruction executed#define EXCEPTION 0x00000040 // Exception#define LIB_LOADED 0x00000080 // New library loaded#define LIB_UNLOADED 0x00000100 // Library unloaded#define INFORMATION 0x00000200 // User-defined information#define PROCESS_ATTACHED 0x00000400 // Attached to running process#define PROCESS_DETACHED 0x00000800 // Detached from process#define PROCESS_SUSPENDED 0x00001000 // Process has been suspended
# patch
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(ea, bytes) | |
ida_bytes.patch_byte(ea, byte) | |
ida_bytes.patch_word(ea, word) | |
ida_bytes.patch_dword(ea, dword) | |
ida_bytes.patch_qword(ea, qword) |
# IDApython 常用脚本
# 打印 IDA 函数列表
import idautils | |
import idc | |
func_addr = [] | |
func_name = [] | |
for i in idautils.Functions(): | |
func_addr.append(i) | |
func_name.append(idc.get_func_name(i)) | |
for i in func_addr: | |
print(f"{hex(i)}, ",end='') | |
print('') | |
for i in func_name: | |
print(f"\"{i}\", ",end='') |
# 批量去除花指令
import idc | |
import ida_bytes | |
import ida_segment | |
def my_nop(addr, endaddr): | |
while addr < endaddr: | |
ida_bytes.patch_byte(addr, 0x90) | |
addr += 1 | |
pattern = ["74 15 75 13 8D 44 24 FC 83 F0 22 3B 04 24 74 0A E8 1F 00 00 00 74 04", | |
"74 0A 75 08 E8 10 00 00 00 EB 04 E8", | |
"48 81 EC 08 03 00 00"] | |
text_seg = ida_segment.get_segm_by_name(".text") | |
start, end = text_seg.start_ea, text_seg.end_ea | |
for i in range(len(pattern)): | |
cur_addr = start | |
end_addr = end | |
while cur_addr < end_addr: | |
cur_addr = idc.find_binary(cur_addr, idc.SEARCH_DOWN, pattern[i]) | |
print("patch address: " + hex(cur_addr)) # 打印提示信息 | |
if cur_addr == idc.BADADDR: | |
break | |
else: | |
my_nop(cur_addr, cur_addr + len(pattern[i].split(' '))) | |
cur_addr = idc.next_head(cur_addr) |
# 去除 BCF 虚假控制流
更多细节请参考 ollvm 三种混淆模式的反混淆思路
# 去除虚假控制流 idapython 脚本 | |
import ida_xref | |
import ida_idaapi | |
from ida_bytes import get_bytes, patch_bytes | |
# 将 mov 寄存器,不透明谓词 修改为 mov 寄存器,0 | |
def do_patch(ea): | |
if get_bytes(ea, 1) == b"\x8B": # mov eax-edi, dword | |
reg = (ord(get_bytes(ea + 1, 1)) & 0b00111000) >> 3 | |
patch_bytes(ea, (0xB8 + reg).to_bytes(1,'little') + b'\x00\x00\x00\x00\x90\x90') | |
else: | |
print('error') | |
# 不透明谓词在.bss 段的范围 | |
seg = ida_segment.get_segm_by_name('.bss') | |
start = seg.start_ea | |
end = seg.end_ea | |
for addr in range(start,end,4): | |
ref = ida_xref.get_first_dref_to(addr) | |
print(hex(addr).center(20,'-')) | |
# 获取所有交叉引用 | |
while(ref != ida_idaapi.BADADDR): | |
do_patch(ref) | |
print('patch at ' + hex(ref)) | |
ref = ida_xref.get_next_dref_to(addr, ref) | |
print('-' * 20) |
# 去除寄存器跳转混淆
仅供参考,需要根据实际情况进行调整!
-
arm64 架构上的
csel-br及cset-br类型寄存器跳转
这个脚本是我在做腾讯游戏安全 2023 的安卓题时写的,更多细节可以参阅细品 sec2023 安卓赛题import ida_segmentimport idautilsimport idcimport ida_bytesfrom keystone import *
def patch_nop(begin, end): # arm64 中的 NOP 指令是 b'\x1F\x20\x03\xD5'
while end > begin:
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(begin, b'\x1F\x20\x03\xD5')
begin = begin + 4
# 获取 text 段的起始地址text_seg = ida_segment.get_segm_by_name(".text")
start, end = text_seg.start_ea, text_seg.end_ea
# start, end = 0x3BA34, 0x3BA80# start, end = 0x37390,0x373B4# 测试 ADRP 指令# start, end = 0x3FCE0, 0x3FD00 # 测试 EQ 情况#start, end = 0x3AA90, 0x3AAA4# start, end = 0x3A078, 0x3A090# 测试 CSET-BR 去除情况current_addr = start# print(text_seg.start_ea,text_seg.end_ea)nop_addr_array_after_finish = [] # 在 CSEL/CSET-BR 结构修复完成后需要 NOP 的指令
while current_addr < end:
# 处理 CSEL-BR 结构if idc.print_insn_mnem(current_addr) == "CSEL":
CSEL_addr = current_addrnop_addr_array_temp = []
nop_addr_array_temp.append(CSEL_addr)
BR_addr = 0
BR_reg = ""
temp_addr = idc.next_head(current_addr)
for _ in range(9): # 向下搜寻 9 条指令,寻找是否有 BR 指令
if idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "BR":
BR_addr = temp_addrBR_reg = idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0)
breakif idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "CSEL":
breaktemp_addr = idc.next_head(temp_addr)
if BR_addr != 0: # 匹配到了 CSEL-BR 结构的汇编,需要去除
# 形如 CSEL X11, X12, X11, GE, 获取 CSEL 后的操作数 op1~3, 以及条件码 condCSEL_op1 = idc.print_operand(CSEL_addr, 0)
CSEL_op2 = idc.print_operand(CSEL_addr, 1)
CSEL_op2_val = -1
CSEL_op3 = idc.print_operand(CSEL_addr, 2)
CSEL_op3_val = -1
CSEL_cond = idc.print_operand(CSEL_addr, 3)
# 读取条件分支语句 CSEL 中要赋值给目标寄存器的两个源寄存器中存储的值temp_addr = idc.prev_head(CSEL_addr)
while (CSEL_op2_val == -1 or CSEL_op3_val == -1) and temp_addr > text_seg.start_ea:
if CSEL_op2 == "XZR": # 如果寄存器的值是 XZR, 说明该值为 0
CSEL_op2_val = 0
if CSEL_op3 == "XZR":
CSEL_op3_val = 0
if idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "MOV":
if idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0)[1::] == CSEL_op2[
1::] and CSEL_op2_val == -1: # 寄存器 X11 和 W11 是同一个寄存器
CSEL_op2_val = idc.get_operand_value(temp_addr, 1)
nop_addr_array_temp.append(temp_addr)
elif idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0)[1::] == CSEL_op3[1::] and CSEL_op3_val == -1:
CSEL_op3_val = idc.get_operand_value(temp_addr, 1)
nop_addr_array_temp.append(temp_addr)
temp_addr = idc.prev_head(temp_addr)
# print(CSEL_op2_val, CSEL_op3_val, hex(current_addr))assert CSEL_op2_val != -1 and CSEL_op3_val != -1
temp_addr = BR_addrjump_array_reg = "" # 存贮跳转表的寄存器名称
jump_array_addr = -1 # 跳转表所在的位置
add_reg = [] # 加到跳转表的值所在的寄存器
add_val = -1 # 加到跳转表的值
while temp_addr > CSEL_addr: # 从后往前找,以 BR 所在的地址开始,CSEL 所在的地址结束,匹配必要的寄存器名称和值
# print(hex(temp_addr),idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr))if idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "ADD" and idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0) == BR_reg:
add_reg.append(idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 1)[1::])
add_reg.append(idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 2)[1::])
nop_addr_array_temp.append(temp_addr)
elif idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "MOV":
if idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0)[1::] in add_reg:
add_val = idc.get_operand_value(temp_addr, 1)
nop_addr_array_temp.append(temp_addr)
elif idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "LDR":
jump_array_reg = idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 1)[1:-1].split(',')[0] # 获取存储跳转表的寄存器名称
nop_addr_array_temp.append(temp_addr)
elif idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "ADRL":
jump_array_reg = idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0)
jump_array_addr = idc.get_operand_value(temp_addr, 1)
nop_addr_array_temp.append(temp_addr)
temp_addr = idc.prev_head(temp_addr)
# 如果在 CSEL-BR 间的指令中没找到跳转表所在的位置,则向上寻找if jump_array_addr == -1:
temp_addr = CSEL_addrwhile temp_addr > text_seg.start_ea:
# print(hex(temp_addr), idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr))if idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "ADRL":
if idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0) == jump_array_reg:
jump_array_addr = idc.get_operand_value(temp_addr, 1)
nop_addr_array_temp.append(temp_addr)
breakelif idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "ADRP": # ADRP 指令,还需要加上另一部分
if idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0) == jump_array_reg:
jump_array_addr = idc.get_operand_value(temp_addr, 1)
nop_addr_array_temp.append(temp_addr)
while temp_addr < text_seg.end_ea:
if idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "ADD":
if idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0) == jump_array_reg:
jump_array_addr += idc.get_operand_value(temp_addr, 2)
nop_addr_array_temp.append(temp_addr)
breaktemp_addr = idc.next_head(temp_addr)
breaktemp_addr = idc.prev_head(temp_addr)
# print(hex(jump_array_addr),hex(add_val))if add_val == -1:
temp_addr = CSEL_addrwhile temp_addr > text_seg.start_ea:
# print(hex(temp_addr), idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr))if idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "MOV":
if idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0)[1::] in add_reg and idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0)[0] == 'X':
add_val = idc.get_operand_value(temp_addr, 1)
nop_addr_array_temp.append(temp_addr)
breaktemp_addr = idc.prev_head(temp_addr)
# 计算出分支跳转的两个位置branch_a = (ida_bytes.get_qword(jump_array_addr + CSEL_op2_val) + add_val) & 0xffffffffffffffff
branch_b = (ida_bytes.get_qword(jump_array_addr + CSEL_op3_val) + add_val) & 0xffffffffffffffff
# print(hex(branch_a), hex(branch_b))# print(CSEL_cond,hex(current_addr))# GE<->LT 有符号大于等于 vs 有符号小于# EQ<->NE 结果相等 vs 结果不相等# CC<->CS 无符号小于 vs 无符号大于等于# HI<->LS 无符号大于 vs 无符号小于等于# if CSEL_cond == "GE":# 构造 B.LT 跳转logic_rev = {"GE": "LT", "LT": "GE", "EQ": "NE", "NE": "EQ", "CC": "CS", "CS": "CC", "HI": "LS", "LS": "HI"}
ks = Ks(KS_ARCH_ARM64, KS_MODE_LITTLE_ENDIAN)
code = ""
if branch_b == idc.next_head(BR_addr): # 判断逻辑不取反
code = f"B.{CSEL_cond} #{hex(branch_a)}"
elif branch_a == idc.next_head(BR_addr): # 判断逻辑取反
code = f"B.{logic_rev[CSEL_cond]} #{hex(branch_b)}"
#print(hex(current_addr), hex(add_val), CSEL_op2_val, CSEL_op3_val, hex(jump_array_addr), code)# 修复 BR 跳转if code != "":
patch_br_byte, count = ks.asm(code, addr=BR_addr)
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(BR_addr, bytes(patch_br_byte))
print(f"fix CSEL-BR at {hex(BR_addr)}")
nop_addr_array_after_finish.extend(nop_addr_array_temp)
current_addr = idc.next_head(BR_addr)
continueelse:
print(f"error! unable to fix CSEL-BR at {hex(current_addr)},branch:{hex(branch_a)}, {hex(branch_b)}")
# 处理 CSET-BR 结构elif idc.print_insn_mnem(current_addr) == "CSET":
CSET_addr = current_addrnop_addr_array_temp = []
nop_addr_array_temp.append(CSET_addr)
BR_addr = 0
BR_reg = ""
temp_addr = idc.next_head(current_addr)
for _ in range(15): # 向下搜寻 15 条指令,寻找是否有 BR 指令
if idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "BR":
BR_addr = temp_addrBR_reg = idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0)
breakelif idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "CSEL":
breakelif idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "RET":
breaktemp_addr = idc.next_head(temp_addr)
if BR_addr != 0: # 匹配到了 CSET-BR 结构的汇编,需要去除
# 形如 CSET W23, NE, 获取 CSET 后的操作数 op1, 以及条件码 condCSET_op1 = idc.print_operand(CSET_addr, 0)
CSET_op1_val = -1
CSET_cond = idc.print_operand(CSET_addr, 1)
temp_addr = BR_addrjump_array_reg = "" # 存贮跳转表的寄存器名称
jump_array_addr = 0 # 跳转表所在的位置
add_reg = [] # 加到跳转表的值所在的寄存器
add_val = 0 # 加到跳转表的值
Lshift_val = -1
while temp_addr > CSET_addr: # 从后往前找,以 BR 所在的地址开始,CSET 所在的地址结束,匹配必要的寄存器名称和值
# print(hex(temp_addr),idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr))if idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "ADD" and idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0) == BR_reg:
add_reg.append(idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 1)[1::])
add_reg.append(idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 2)[1::])
nop_addr_array_temp.append(temp_addr)
elif idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "MOVK":
if idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0)[1::] in add_reg:
add_val += (idc.get_operand_value(temp_addr, 1) << 16)
elif idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "MOV":
if idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0)[1::] in add_reg:
add_val += idc.get_operand_value(temp_addr, 1)
nop_addr_array_temp.append(temp_addr)
elif idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "LDR":
LDR_temp = idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 1)[1:-1].split(',')
jump_array_reg = LDR_temp[0] # 获取存储跳转表的寄存器名称
if len(LDR_temp) == 3:
Lshift_val = int(LDR_temp[2][-1:])
nop_addr_array_temp.append(temp_addr)
elif idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "ADRL":
jump_array_reg = idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0)
jump_array_addr = idc.get_operand_value(temp_addr, 1)
nop_addr_array_temp.append(temp_addr)
elif idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "LSL":
if idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0)[1::] == CSET_op1[1::]:
Lshift_val = idc.get_operand_value(temp_addr, 2)
temp_addr = idc.prev_head(temp_addr)
# 如果在 CSET-BR 间的指令中没找到跳转表所在的位置,则向上寻找if jump_array_addr == 0:
temp_addr = CSET_addrwhile temp_addr > text_seg.start_ea:
# print(hex(temp_addr), idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr))if idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "ADRL":
if idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0) == jump_array_reg:
jump_array_addr = idc.get_operand_value(temp_addr, 1)
nop_addr_array_temp.append(temp_addr)
breakelif idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "ADRP": # ADRP 指令,还需要加上另一部分
if idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0) == jump_array_reg:
jump_array_addr = idc.get_operand_value(temp_addr, 1)
nop_addr_array_temp.append(temp_addr)
while temp_addr < text_seg.end_ea:
if idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "ADD":
if idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0) == jump_array_reg:
jump_array_addr += idc.get_operand_value(temp_addr, 2)
nop_addr_array_temp.append(temp_addr)
breaktemp_addr = idc.next_head(temp_addr)
breaktemp_addr = idc.prev_head(temp_addr)
# print(hex(jump_array_addr),hex(add_val))# 向上寻找加到跳转表的值if add_val == 0:
temp_addr = CSET_addrwhile temp_addr > text_seg.start_ea:
# print(hex(temp_addr), idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr))if idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "MOV":
if idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0)[1::] in add_reg:
add_val = idc.get_operand_value(temp_addr, 1)
nop_addr_array_temp.append(temp_addr)
breakelif idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "MOVK": # 形如 MOV W9, #0x76BC;MOVK W9, #0x4C48,LSL#16; 的形式
if idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0)[1::] in add_reg:
# print(hex(add_val))add_val = (idc.get_operand_value(temp_addr, 1) << 16)
# print(hex(add_val))while temp_addr > text_seg.start_ea:
if idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "MOV":
if idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0)[1::] in add_reg:
add_val += idc.get_operand_value(temp_addr, 1)
# print(hex(add_val))breaktemp_addr = idc.prev_head(temp_addr)
breaktemp_addr = idc.prev_head(temp_addr)
# print(hex(current_addr))# 计算出分支跳转的两个位置branch_a = (ida_bytes.get_qword(jump_array_addr + (1 << Lshift_val)) + add_val) & 0xffffffffffffffff
branch_b = (ida_bytes.get_qword(jump_array_addr + (0 << Lshift_val)) + add_val) & 0xffffffffffffffff
# print(hex(branch_a), hex(branch_b))# print(CSEL_cond,hex(current_addr))# GE<->LT 有符号大于等于 vs 有符号小于# EQ<->NE 结果相等 vs 结果不相等# CC<->CS 无符号小于 vs 无符号大于等于# HI<->LS 无符号大于 vs 无符号小于等于# if CSEL_cond == "GE":# 构造 B.LT 跳转logic_rev = {"GE": "LT", "LT": "GE", "EQ": "NE", "NE": "EQ", "CC": "CS", "CS": "CC", "HI": "LS", "LS": "HI"}
ks = Ks(KS_ARCH_ARM64, KS_MODE_LITTLE_ENDIAN)
code = ""
if branch_b == idc.next_head(BR_addr): # 判断逻辑不取反
code = f"B.{CSET_cond} #{hex(branch_a)}"
elif branch_a == idc.next_head(BR_addr): # 判断逻辑取反
code = f"B.{logic_rev[CSET_cond]} #{hex(branch_b)}"
# print(hex(current_addr),add_reg,hex(add_val),CSET_op1,CSET_op1_val,jump_array_reg,hex(jump_array_addr),Lshift_val,code)# 修复 BR 跳转if code != "":
patch_br_byte, count = ks.asm(code, addr=BR_addr)
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(BR_addr, bytes(patch_br_byte))
print(f"fix CSET-BR at {hex(BR_addr)}")
nop_addr_array_after_finish.extend(nop_addr_array_temp)
current_addr = idc.next_head(BR_addr)
continueelse:
print(f"error! unable to fix CSET-BR at {hex(current_addr)},branch:{hex(branch_a)}, {hex(branch_b)}")
current_addr = idc.next_head(current_addr)
for addr in nop_addr_array_after_finish:
patch_nop(addr, addr + idc.get_item_size(addr))
-
x86_64 架构的
jmp rax类型寄存器跳转
例题点这里下载 ACTF-obfuseimport ida_segmentimport idautilsimport idcimport ida_bytesimport binasciiimport refrom keystone import *
def patch_nop(addr, endaddr):
while addr < endaddr:
ida_bytes.patch_byte(addr, 0x90)
addr += 1
# 获取 text 段的起始地址text_seg = ida_segment.get_segm_by_name(".text")
start, end = text_seg.start_ea, text_seg.end_ea
# start, end = 0x41143D,0x41145F# 测试 call rax#start, end = 0x411489,0x411498# 测试 jmp rax case1# start, end = 0x411568, 0x411575 # 测试 jmp rax case2#start, end = 0x410EC0,0x412670# 去除 check 函数的混淆#start, end = 0x410EC0,0x412670# 在 check 中测试 jmp rax case2current_addr = startcall_table = 0x67F1A0 # call rax 跳转表地址
'''这是一个call rax基本块 需要去除mov rax, [rax+14E8h];call rax
mov rax, [rax+14E8h]
movzx edi, byte ptr [rbp+var_50+6]
mov edx, offset dword_674040
mov esi, 1
lea rcx, [rbp+var_120]
mov r8d, 2AE8944Ah
call rax
处理后应为如下形式
movzx edi, byte ptr [rbp+var_50+6]
mov edx, offset dword_674040
mov esi, 1
lea rcx, [rbp+var_120]
mov r8d, 2AE8944Ah
call sub_xxxxxx
'''
while current_addr <= end:
#print(hex(current_addr))# 处理 call rax 结构if idc.print_insn_mnem(current_addr) == "call" and idc.print_operand(current_addr, 0) == "rax":
# print("call rax")call_rax_addr = current_addrmov_rax_xxxh_addr = -1
call_func_addr = -1
# 获取需要跳转的地址temp_addr = call_rax_addrcount = 1
while temp_addr >= start and count<30:
if idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "mov" and idc.print_operand(temp_addr,
0) == "rax" and "rax" in idc.print_operand(
temp_addr, 1):
mov_rax_xxxh_addr = temp_addr# 获取 [rax+14E8h] 中的 14E8 十六进制字符串tmp_call_table_offset_re_result = re.findall(r'\[\w+\+([\da-fA-F]+)', idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 1))
if tmp_call_table_offset_re_result:
tmp = tmp_call_table_offset_re_result[0]
#print(tmp)if len(tmp)%2==1:
if tmp.startswith('0'):
tmp = tmp[1::]
else:
tmp = '0'+tmp
call_table_offset = binascii.a2b_hex(tmp)
else:
breakcall_table_offset = int.from_bytes(call_table_offset, 'big')
call_func_addr = ida_bytes.get_dword(call_table + call_table_offset)
breaktemp_addr = idc.prev_head(temp_addr)
count = count+1
# print(hex(call_func_addr))if call_rax_addr == -1 or mov_rax_xxxh_addr == -1 or call_func_addr == -1:
current_addr = idc.next_head(current_addr)
continue# 准备 patchmovRAX_callRAX_patch = b''
# print(hex(idc.next_head(mov_rax_xxxh_addr)),hex(call_rax_addr))ea = idc.next_head(mov_rax_xxxh_addr)
while ea < call_rax_addr:
size = idc.next_head(ea) - ea
#print(ida_bytes.get_bytes(ea, size))movRAX_callRAX_patch += ida_bytes.get_bytes(ea, size)
ea = idc.next_head(ea)
# 计算跳转到的地址if call_func_addr != -1:
ks = Ks(KS_ARCH_X86, KS_MODE_64)
code = f"call {call_func_addr}"
patch_call_rax_byte, count = ks.asm(code, addr=(mov_rax_xxxh_addr + len(movRAX_callRAX_patch)))
#print(call_func_addr, code, patch_call_rax_byte)else:
continuemovRAX_callRAX_patch += bytes(patch_call_rax_byte)
# print(movRAX_callRAX_patch)ida_bytes.patch_bytes(mov_rax_xxxh_addr, b'\x90' * (idc.next_head(call_rax_addr) - mov_rax_xxxh_addr))
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(mov_rax_xxxh_addr, movRAX_callRAX_patch)
print(f"fix call rax at {hex(call_rax_addr)}")
# 处理 jmp rax 结构'''考虑两种情况 此时需要先获取rcx
一:
mov rax, cs:qword_67CA28
mov ecx, 0ADAE163Ch
add rax, rcx
jmp rax
二:
mov rax, cs:qword_67CA30
add rax, 5C65CCC7h
jmp rax
'''
if idc.print_insn_mnem(current_addr) == "jmp" and idc.print_operand(current_addr, 0) == "rax":
# print("jmp rax")mov_rax_qword_xxx_addr = -1
mov_reg_xxx_addr = -1
add_rax_xxx_addr = -1
jmp_rax_addr = current_addradd_num1 = -1
add_num2 = -1
# 获取加上的第一个数temp_addr = jmp_rax_addrcount = 1
while temp_addr >= start and count<30:
if idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "mov" and idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0) == "rax":
mov_rax_qword_xxx_addr = temp_addrtmp = re.findall(r'cs:qword_([0-9A-Fa-f]+)', idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 1))
if tmp:
add_num1_addr = tmp[0]
add_num1_addr = int.from_bytes(binascii.a2b_hex(add_num1_addr), 'big')
add_num1 = ida_bytes.get_qword(add_num1_addr)
else:
break#print(add_num1_addr)breaktemp_addr = idc.prev_head(temp_addr)
count = count+1
# 获取加上的第二个数temp_addr = jmp_rax_addrcount = 1
while temp_addr >= start and count<30:
if idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr) == "add" and idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0) == "rax":
add_rax_xxx_addr = temp_addr# 如果直接加上一个数if not idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 1).endswith('x'):
add_num2 = idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 1)
# 如果这个数是通过寄存器例如 ecx 赋值的else:
tmp_add_num2_reg = idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 1)
temp_addr_2 = temp_addrcount2 = 1
while temp_addr_2 >= start and count2<30:
# print(idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr),idc.print_operand(temp_addr, 0)[1::],tmp_add_num2_reg[1::])if idc.print_insn_mnem(temp_addr_2) == "mov" and idc.print_operand(temp_addr_2, 0)[
1::] == tmp_add_num2_reg[1::]:
add_num2 = idc.print_operand(temp_addr_2, 1)
mov_reg_xxx_addr = temp_addr_2breaktemp_addr_2 = idc.prev_head(temp_addr_2)
count2=count2+1
try:
add_num2 = add_num2.strip('h')
if len(add_num2) % 2 == 1:
if add_num2.startswith('0'):
add_num2 = add_num2[1::]
else:
add_num2 = '0' + add_num2
add_num2 = int.from_bytes(binascii.a2b_hex(add_num2), 'big')
#print(add_num2)except:
breakbreaktemp_addr = idc.prev_head(temp_addr)
count = count+1
if add_num1 == -1 or add_num2 == -1 or mov_rax_qword_xxx_addr == -1 or add_rax_xxx_addr == -1 or jmp_rax_addr == -1:
#print(add_num1,add_num2,mov_rax_qword_xxx_addr,add_rax_xxx_addr,jmp_rax_addr)current_addr = idc.next_head(current_addr)
continue# 准备 patchmovRAX_jmpRAX_patch = b''
#print(hex(idc.next_head(mov_rax_xxxh_addr)), hex(call_rax_addr))should_pass_addr = [mov_rax_qword_xxx_addr, mov_reg_xxx_addr, add_rax_xxx_addr, jmp_rax_addr]
ea = mov_rax_qword_xxx_addrwhile ea < jmp_rax_addr:
if ea not in should_pass_addr:
size = idc.next_head(ea) - ea
# print(ida_bytes.get_bytes(ea, size))movRAX_jmpRAX_patch += ida_bytes.get_bytes(ea, size)
ea = idc.next_head(ea)
# 计算跳转到的地址#print(hex(add_num1), add_num2)jmp_addr = (add_num1 + add_num2) & 0xffffffff
ks = Ks(KS_ARCH_X86, KS_MODE_64)
code = f"jmp {jmp_addr}"
patch_call_rax_byte, count = ks.asm(code, addr=(mov_rax_qword_xxx_addr + len(movRAX_jmpRAX_patch)))
# print(call_func_addr, code, patch_call_rax_byte)movRAX_jmpRAX_patch += bytes(patch_call_rax_byte)
# print(movRAX_callRAX_patch)ida_bytes.patch_bytes(mov_rax_qword_xxx_addr, b'\x90' * (idc.next_head(jmp_rax_addr) - mov_rax_qword_xxx_addr))
ida_bytes.patch_bytes(mov_rax_qword_xxx_addr, movRAX_jmpRAX_patch)
print(f"fix jmp rax at {hex(jmp_rax_addr)}")
current_addr = idc.next_head(current_addr)
#patch_nop(0x410FB3,0x41142C)
# 参考资料
-
ida python 使用
-
idapython 笔记学习
-
在 PyCharm 中写 IDAPython 脚本